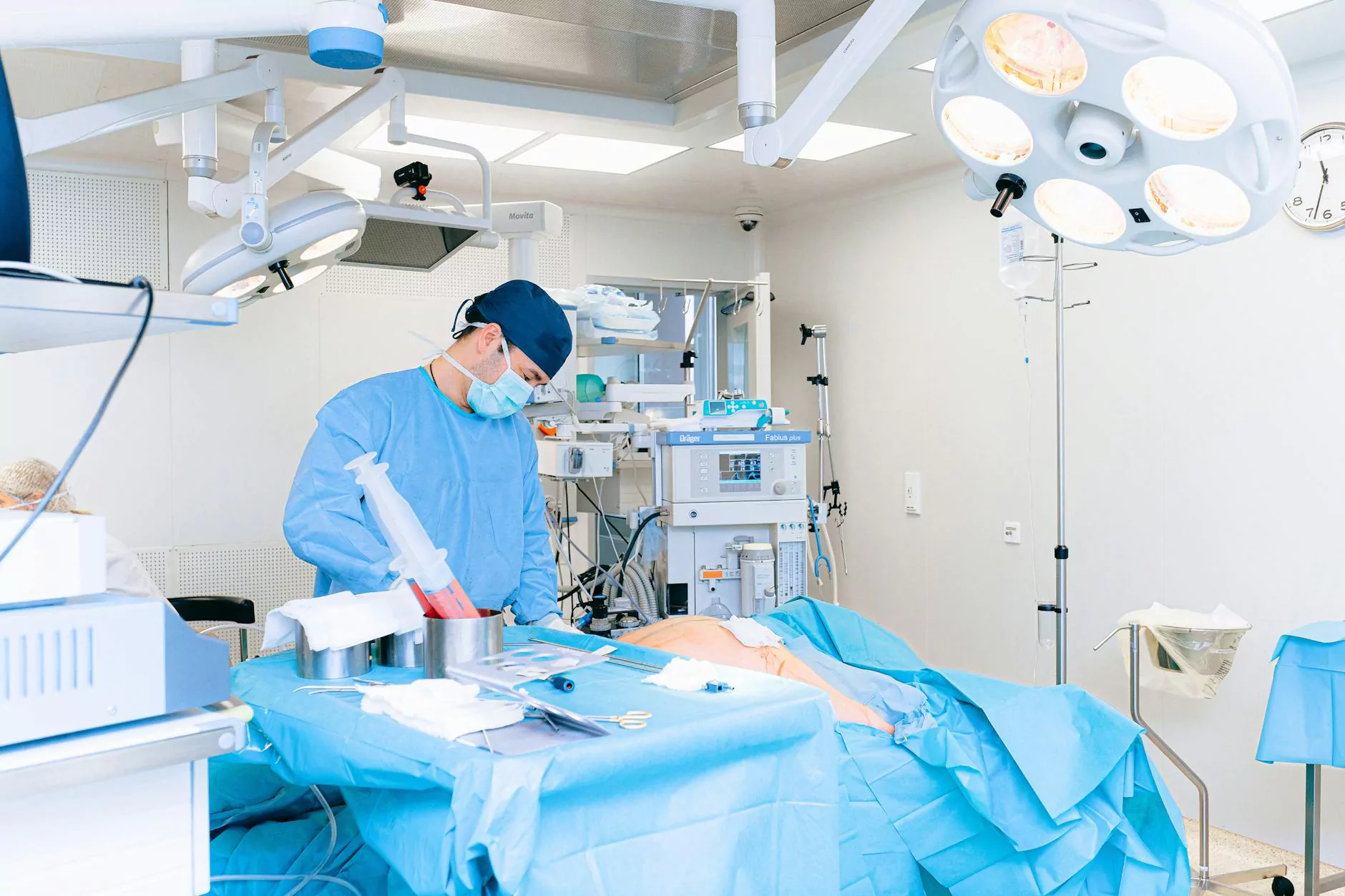
Understanding Recurrent Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is a serious medical condition that involves the presence of air in the pleural space, leading to a lung collapse. When this condition occurs repeatedly, it is termed recurrent pneumothorax. It is crucial for individuals experiencing this condition to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to them.
What Causes Recurrent Pneumothorax?
Recurrent pneumothorax can arise from various underlying issues. Some of the most common causes include:
- Chronic Lung Diseases: Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cystic fibrosis.
- Tall and Thin Physique: Young males, particularly those who are tall and thin, are at higher risk.
- Previous Lung Surgery: Surgical interventions on the lung can lead to complications including pneumothorax.
- Barometric Pressure Changes: Rapid changes in pressure can precipitate a pneumothorax, particularly in divers or mountain climbers.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic conditions such as Marfan syndrome can predispose individuals to pneumothorax.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Being able to identify the symptoms of recurrent pneumothorax is vital for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden Chest Pain: Often sharp and localized to one side of the chest.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless, which can occur suddenly.
- Rapid Breathing: Increased respiratory rate, sometimes accompanied by anxiety.
- Dry Cough: An unproductive cough can sometimes occur.
Diagnosis of Recurrent Pneumothorax
If recurrent pneumothorax is suspected, immediate medical evaluation is necessary. The diagnosis is typically made through:
- Physical Examination: A clinician will assess for signs such as decreased breath sounds.
- X-rays: Chest X-rays are essential for visualizing the presence of a pneumothorax.
- CT Scans: More detailed imaging, providing better insights into lung structure.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Pneumothorax
Treatment for recurrent pneumothorax is often necessary to prevent lung collapse and manage symptoms effectively. Various treatment modalities include:
1. Observation and Monitoring
In cases of small, asymptomatic pneumothorax, doctors may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular follow-ups will be essential to monitor the condition.
2. Needle Aspiration
For a more significant pneumothorax or if symptoms are considerable, needle aspiration may be performed. This procedure involves using a needle to withdraw air from the pleural space.
3. Chest Tube Insertion
For larger pneumothoraces, a chest tube may be inserted to facilitate continuous draining of air from the pleural cavity. This method is more invasive but effective for managing larger collections of air.
4. Surgical Interventions
Persistent or recurrent cases of pneumothorax may necessitate surgical options, which can include:
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive approach where small incisions are made, and a camera is used for the procedure.
- Pleurodesis: A procedure that involves creating adhesion between the lung and the pleura to prevent further pneumothoraces.
- Open Thoracotomy: In more extreme cases, traditional open surgery might be required.
Long-term Management of Recurrent Pneumothorax
Managing recurrent pneumothorax extends beyond immediate treatment. Long-term strategies should focus on:
- Lung Health Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider to assess lung health.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: Identifying and avoiding activities that can increase the risk of recurrence, such as scuba diving or high-altitude activities.
- Medications: In certain cases, bronchodilators or corticosteroids may be prescribed to manage underlying lung conditions.
Innovative Treatments and Research
The landscape of treatment for recurrent pneumothorax is continuously evolving. Ongoing research aims to identify new therapies and refine existing procedures, including:
- Biological Agents: Studies are exploring the use of biological agents to encourage pleural adhesion and reduce recurrence rates.
- Improved Surgical Techniques: Technological advancements in surgical procedures aim to minimize recovery times and complications.
- Telemedicine: Enhanced access to healthcare providers for post-treatment monitoring and support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding recurrent pneumothorax treatment is crucial for patients facing this medical challenge. Early recognition and appropriate management can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life. Patients should engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers to determine the best personalized treatment strategy.
For more detailed information and personalized care options, consider scheduling a consultation with experts from Neumark Surgery. Our dedicated team of healthcare professionals is equipped to provide the support and treatment necessary for managing recurrent pneumothorax and associated lung health concerns.
recurrent pneumothorax treatment